Assessing our applications is important because it helps us understand what security controls are efficient, and which ones are not. Whether you call it a vulnerability assessment or a penetration test, often used interchangeably, the value is important. Vulnerability assessments and penetration tests are different. The goals are often different. Many times the techniques are different as well. its s important to understand what you are trying to accomplish.
Today, many applications are spread across multiple technologies and platforms. Unlike in the past, when most applications were just on the web, now many also reside on mobile devices and even other internet of things devices. We must understand how these pieces all fit together and verify that they do not open potential issues for each other. Have a look at the following image showing some of the different components that can be a part of the same application.
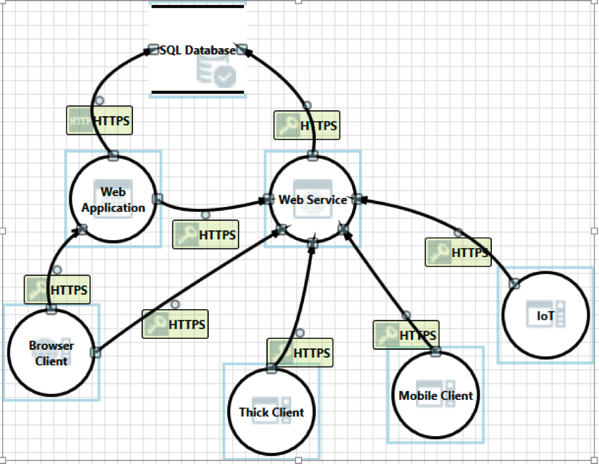
Unfortunately, when we see a security assessment performed, we typically focus on one component at a time. We know we need to test the web and mobile applications, but we do them at different times. There are many reasons for this to happen, for example different release schedules, but it is something we must consider.
Look back at the picture above and notice that there are shared APIs and data sources. Data from one application maybe be updated from another. When we perform an assessment on just one of the pieces, we lose the ability to see the effects the other pieces have. Lets look at an example:
Years ago, I worked on a system that had web, windows, and mobile components to it. The web team did an excellent job of limiting input into their application. They were fairly well protected against cross-site scripting payloads, often just by the built in frameworks they used. Unfortunately, the mobile application (which was not effected by XSS) didn’t do as good of a job with their input validation. It was very easy to put XSS payloads into the mobile application and sync them to the server. Then, switching back to the web client, viewing that data would execute the XSS.
This was a multi-part lesson. First, the web team learned that they can’t trust the data in the database. Even though they were fairly well protected against inputs in their application, there were other components updating that same data source. They had to start looking at output encoding their data when they sent it to the browser. Second, it highlighted the fact that these components don’t exist in a silo. They are working together to provide a complete solution. We couldn’t get away with just testing each one on its own. There was a whole class of issues that were left out during the testing phase.
I have seen this time and time again during application assessments and it will only get more common. Each component is different. They react different to different inputs. They store data differently. You never know when that one piece of data, hard-coded into the mobile application, will lead to a compromise on the web application.
During our development and QA stages we will have time to focus on a sole component to make sure that it is functioning as expected. However, we have to identify ways to verify that the components are working together as expected. This doesn’t start with testing, it actually starts with design and understanding the different components. Mapping out the data and how/where it is used. Understanding what that data means to different components can help us understand how it may be used against other components.
If you are getting ready to perform an application penetration test or other security assessments against your applications, consider putting them all into scope. You may be surprised at what may be found.